Route Configuration
Routes are the core component of Javelin that define how incoming requests are processed, which models they connect to, and what policies are applied. This guide explains the two route types — Unified and Custom — and how to configure each, including advanced settings like rate limits, retries, and team ownership.
Unified Route
Unified routes offer a simplified interface that dynamically handles various model types through a single logical endpoint. Ideal for centralized model management and A/B testing.
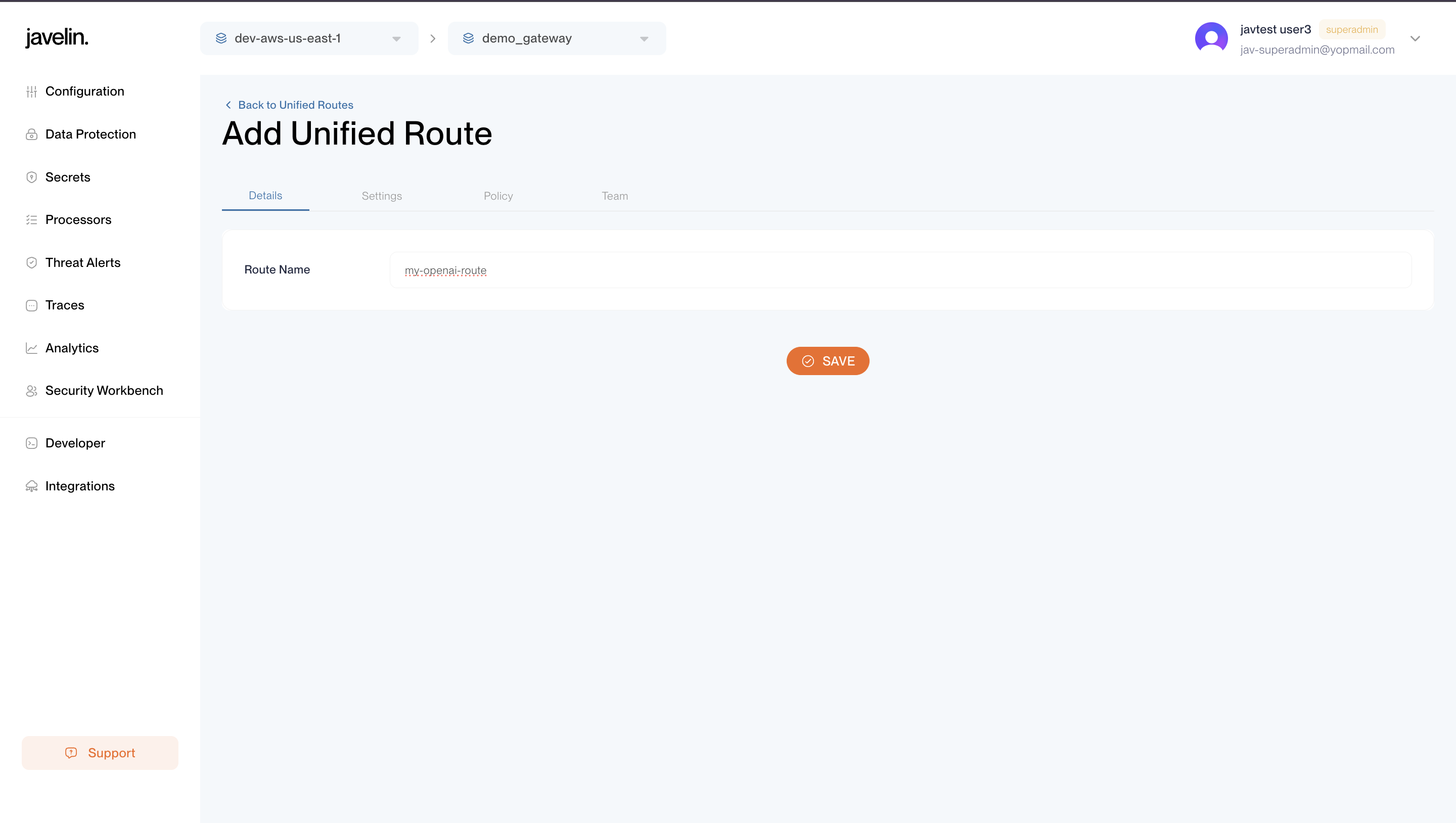
Example: Unified Route (cURL)
curl -X POST "https://api-dev.javelin.live/v1/chat/completions" \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-H "Authorization: Bearer $OPENAI_API_KEY" \
-H "X-Javelin-Apikey: $JAVELIN_API_KEY" \
-H "X-Javelin-route: demo-unified-route" \
-d '{
"model": "gpt-3.5-turbo",
"messages": [
{"role": "system", "content": "You are a helpful assistant."},
{"role": "user", "content": "Tell me about Javelin."}
],
"temperature": 0.7,
"max_tokens": 150
}'
Fields
| name | type | required | default | description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| name | string | yes | — | Unique identifier for the route. Used to reference the unified endpoint. |
All other configuration is automatically managed behind the scenes.
Custom Route
Custom routes allow detailed control over model selection, request handling, and routing logic. Use these for specialized applications, custom models, or fine-tuned behaviors.
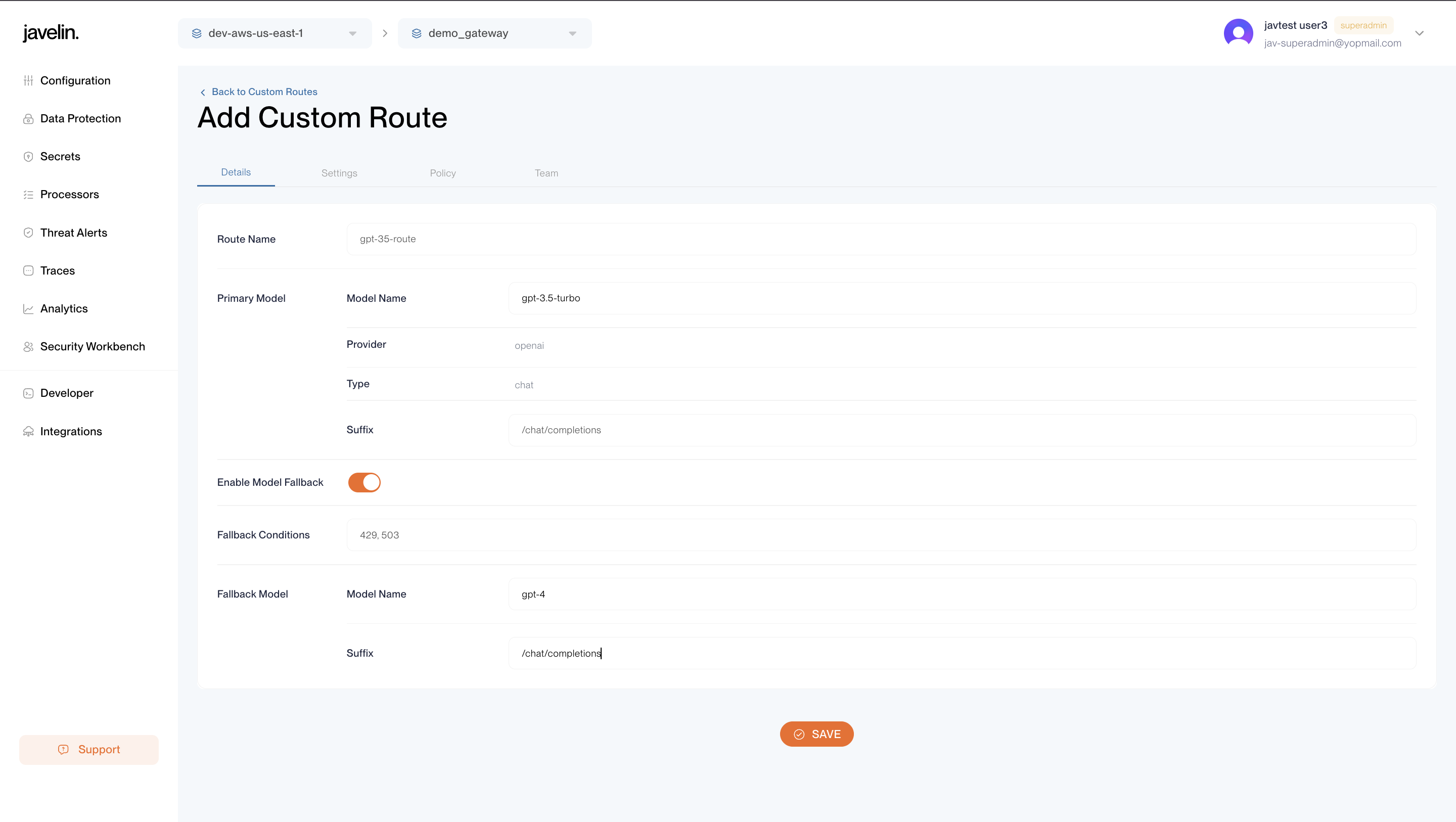
Route Configuration Structure
name: demo-route
type: chat
models:
- name: gpt-3.5-turbo
provider: openai
suffix: /chat/completions
config:
rate_limit: 5
retries: 2
organization: acme-corp
owner: jane.doe@example.com
policy:
enabled: true # Enforces route-level policies instead of application defaults
...
enabled: true
Fields
| name | type | required | default | description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| name | string | yes | — | Unique name identifying the route. |
| type | string | yes | — | Defines the route's purpose: chat, completions, embeddings, etc. |
Models
| name | type | required | default | description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| name | string | yes | — | Name of the model to be used (e.g., gpt-3.5-turbo). |
| provider | string | yes | — | LLM provider name (e.g., openai, anthropic, cohere). |
| suffix | string | no | — | Optional suffix for specific endpoint customization. |
Shared Configuration
Both Unified Routes and Custom Routes share the following configuration sections:
- Settings Config: Controls system-level behavior like
rate_limitandretries. - Team Config: Includes organizational metadata like
ownerandorganization. - Policy Config: Same as Policy configuration under Applications, but specific to a route.
These shared configs ensure consistent management across all route types.
Settings Config
These define operational controls like throughput and retry behavior.
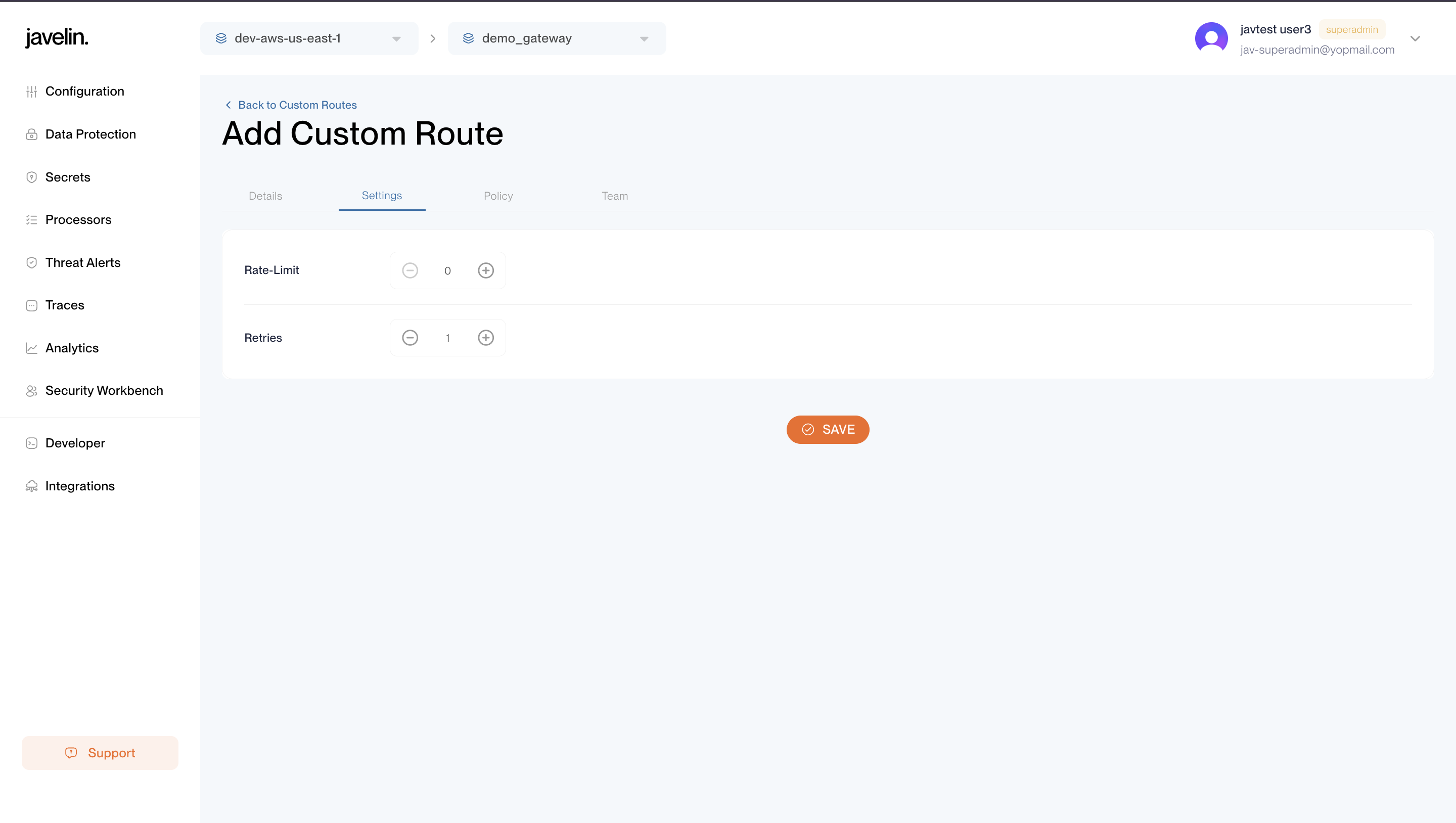
| name | type | required | default | description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| rate_limit | number | no | 0 | Max requests per second allowed through the route. |
| retries | number | no | 1 | Number of retry attempts if the provider fails (e.g., returns 503). |
Team Config
These values define ownership and access attribution for auditing and visibility.
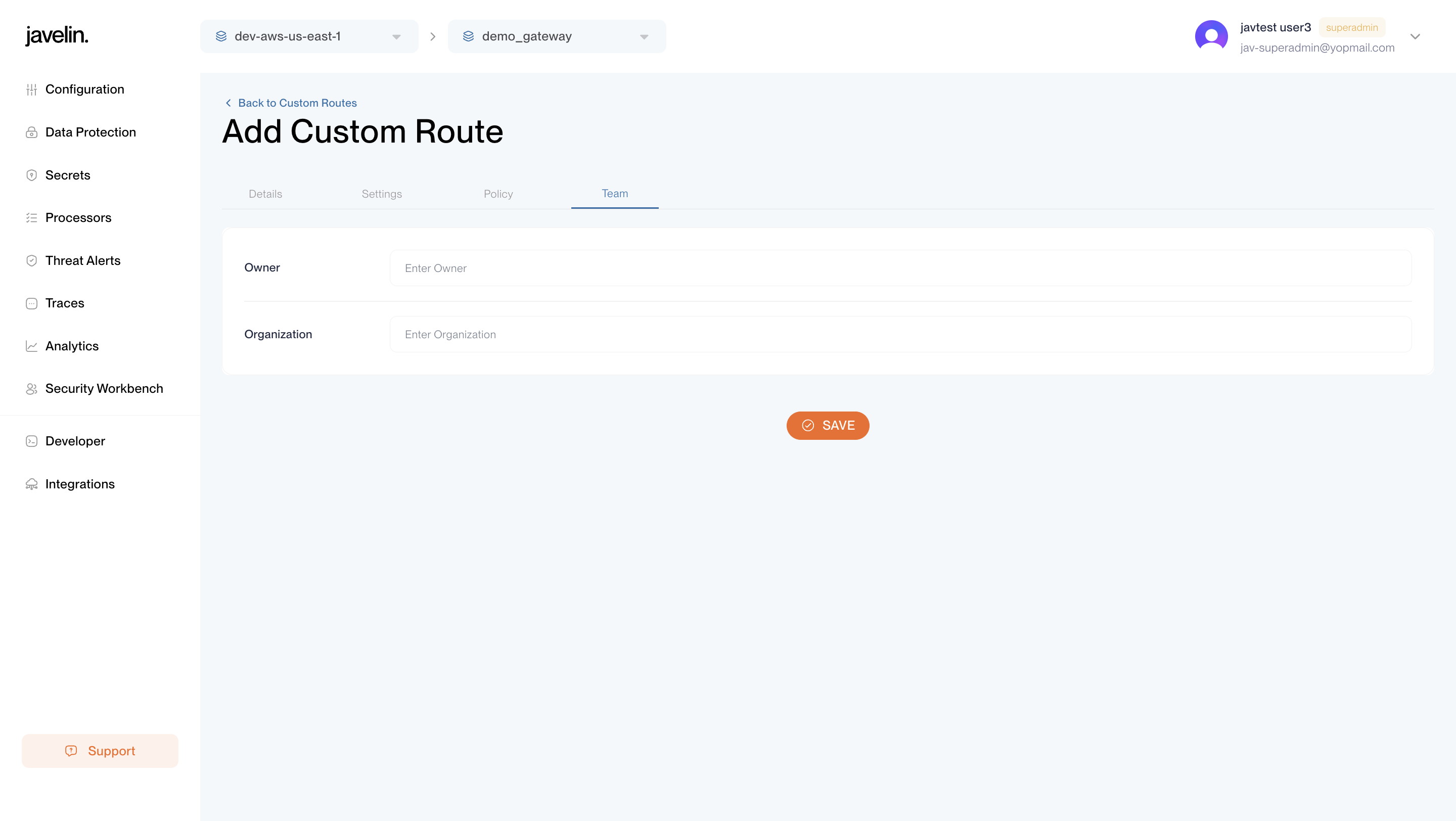
| name | type | required | default | description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| owner | string | no | — | Email or identifier for the route owner. |
| organization | string | no | — | Organization that owns or manages the route. |
Policy Config
Policy configuration allows you to enforce content safety, privacy, compliance, and moderation behaviors at the route level. These policies are available for both Unified and Custom routes and are applied during request processing.
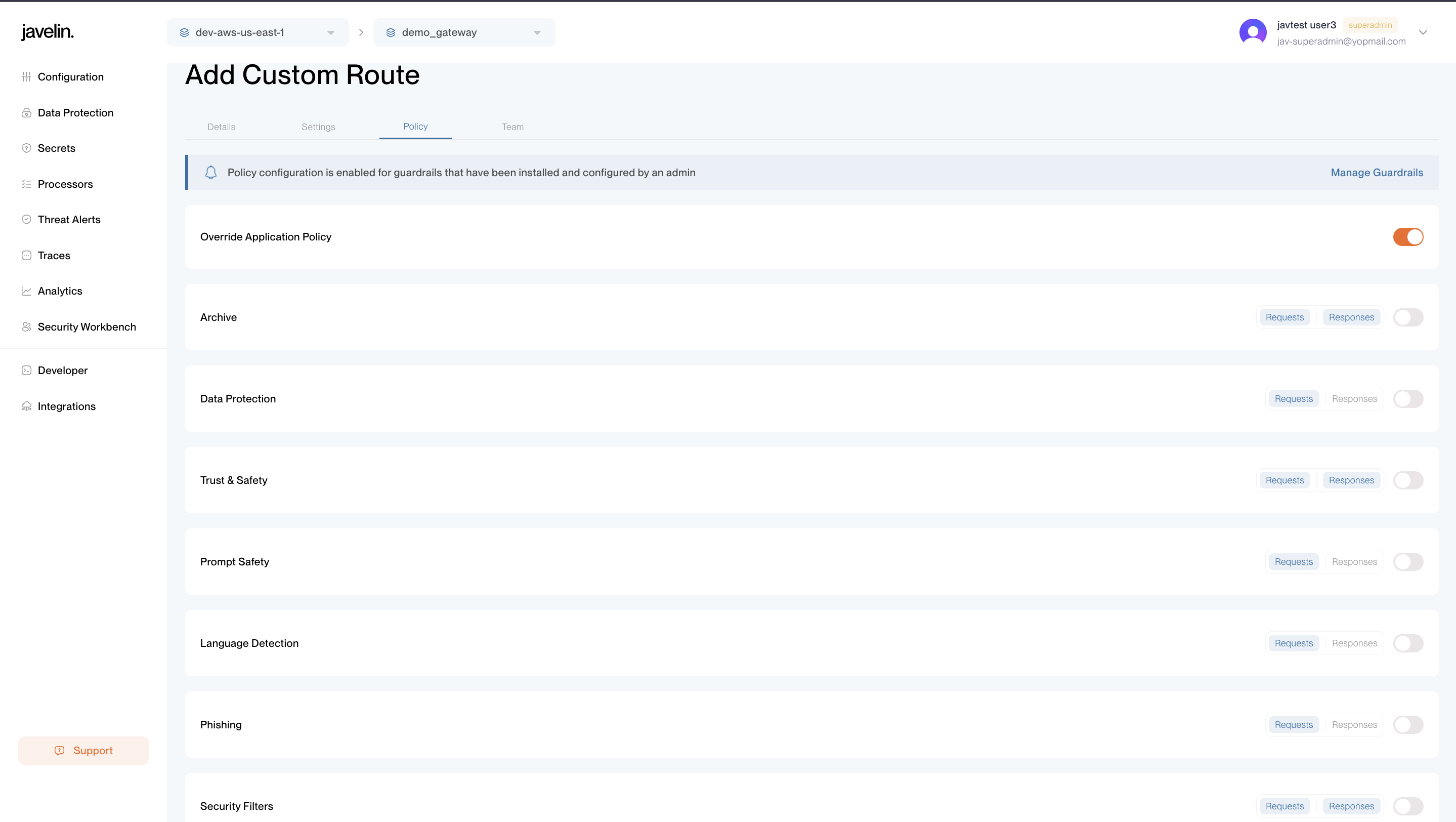
Policy tab under routes is only accessible to Super Admin users.
The “Override Application Policies” toggle allows you to enforce custom policy rules at the route level. When enabled, the route will use its own policy settings instead of inheriting them from the application configuration.
To learn more about configuring policies in detail, see Policy Configuration.