MCP Guides
This guide explains how to create and manage MCP Registries in Javelin, configure policies, enable/disable tools, and integrate them with your Applications.
Creating an MCP Registry
- Navigate to the MCP Registries page within your gateway.
- Click Add MCP Registry button.
- In the Details tab, fill in the required fields (see Details Tab for a complete description of each field).
- Click Save to create the registry.
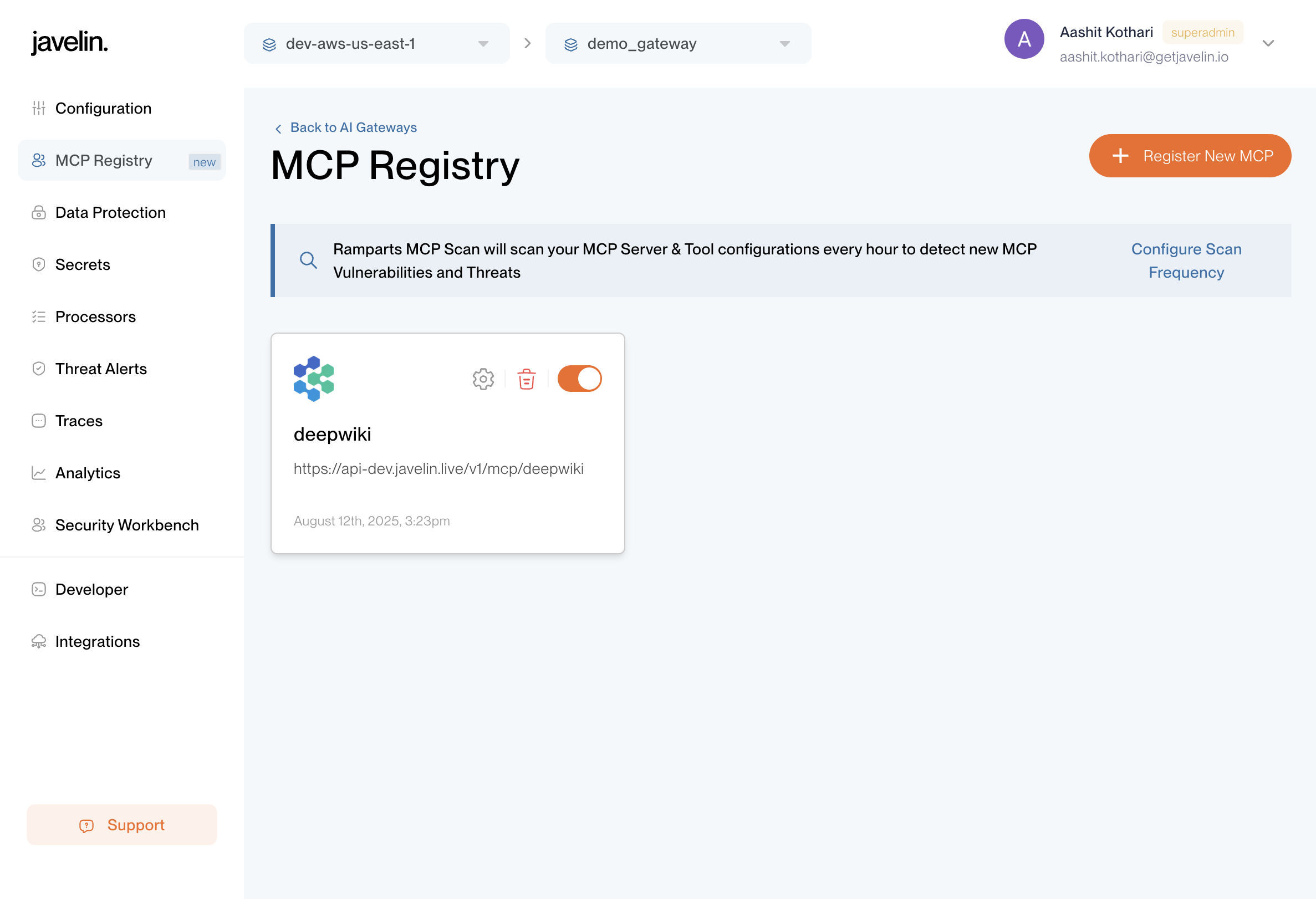
Once an MCP Registry is created, it will appear in the MCP Registries list.
From here, selecting a registry takes you to its dedicated page where you can configure and manage it further.
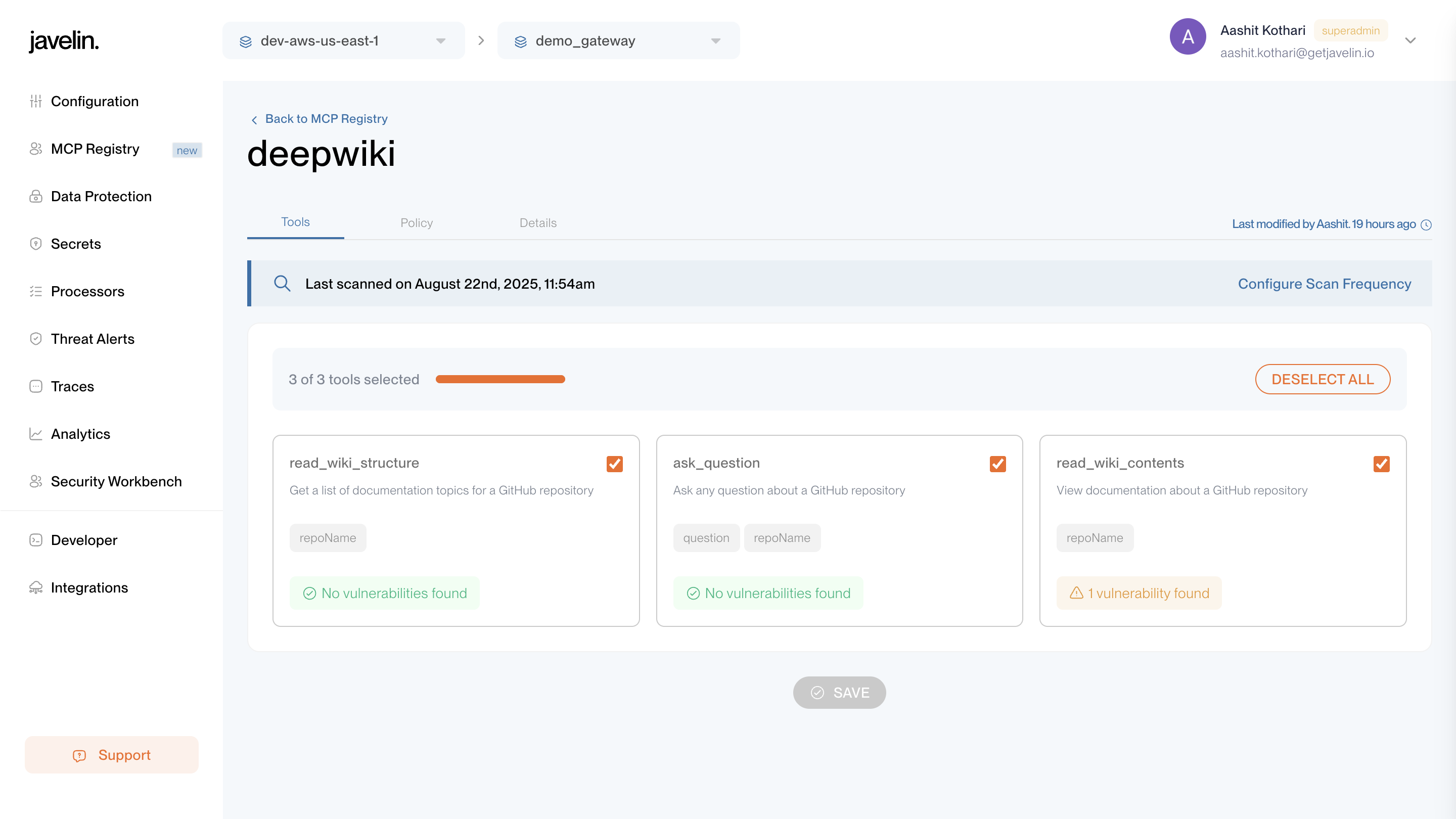
Tools Tab
The Tools tab allows you to:
- View all tools exposed by the registered MCP server.
- Enable or disable individual tools for controlled access.
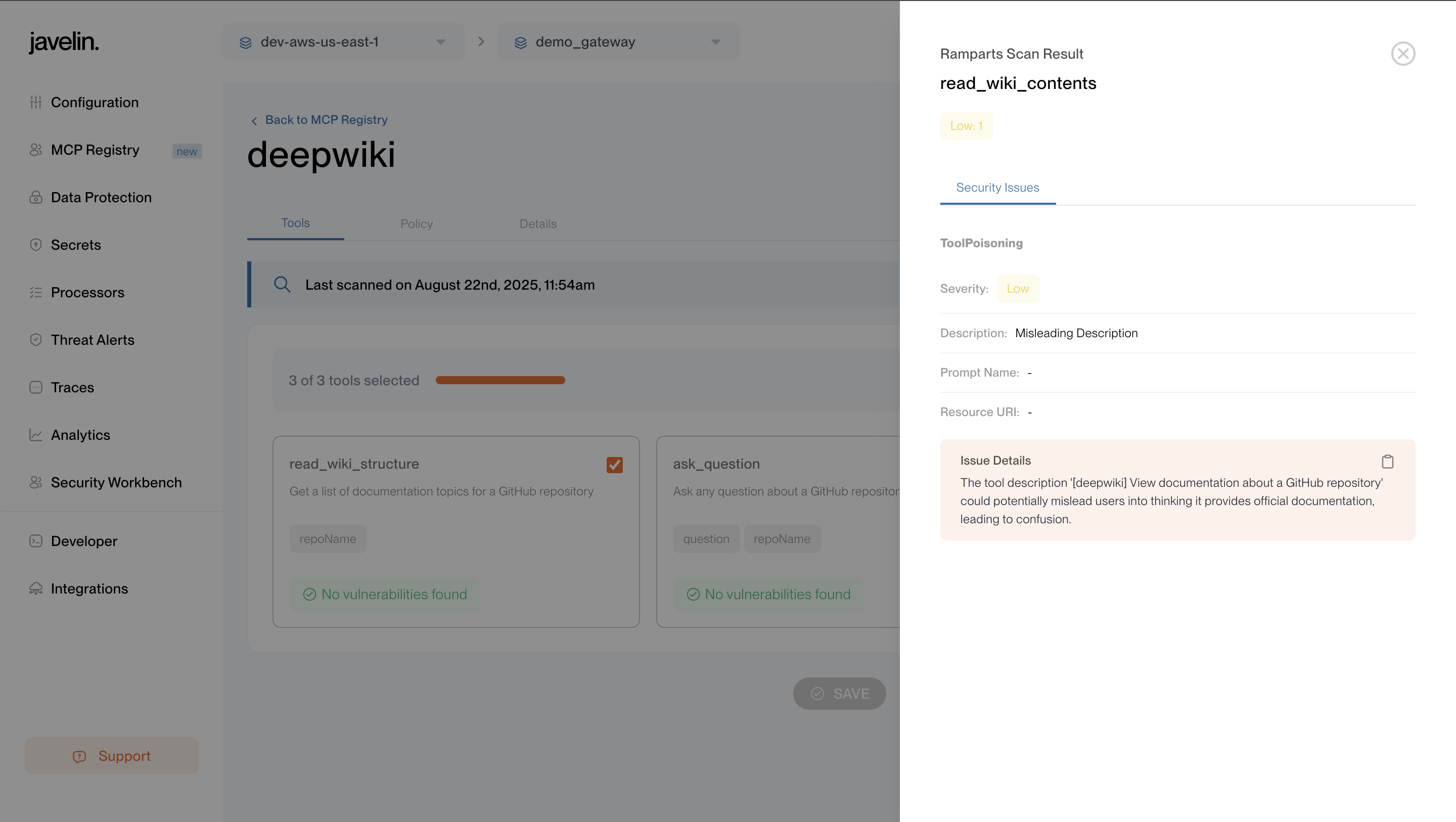
- See Vulnerability scan results for each tool.
Whenever you enable/disable a tool or open the Tools tab, Javelin automatically runs a vulnerability scan on that tool.
The results are displayed directly in this tab, showing potential security vulnerabilities.
This ensures that every tool made available through MCP is continuously assessed for risk, giving developers and admins clear visibility into tool security posture before use.
Policy Tab
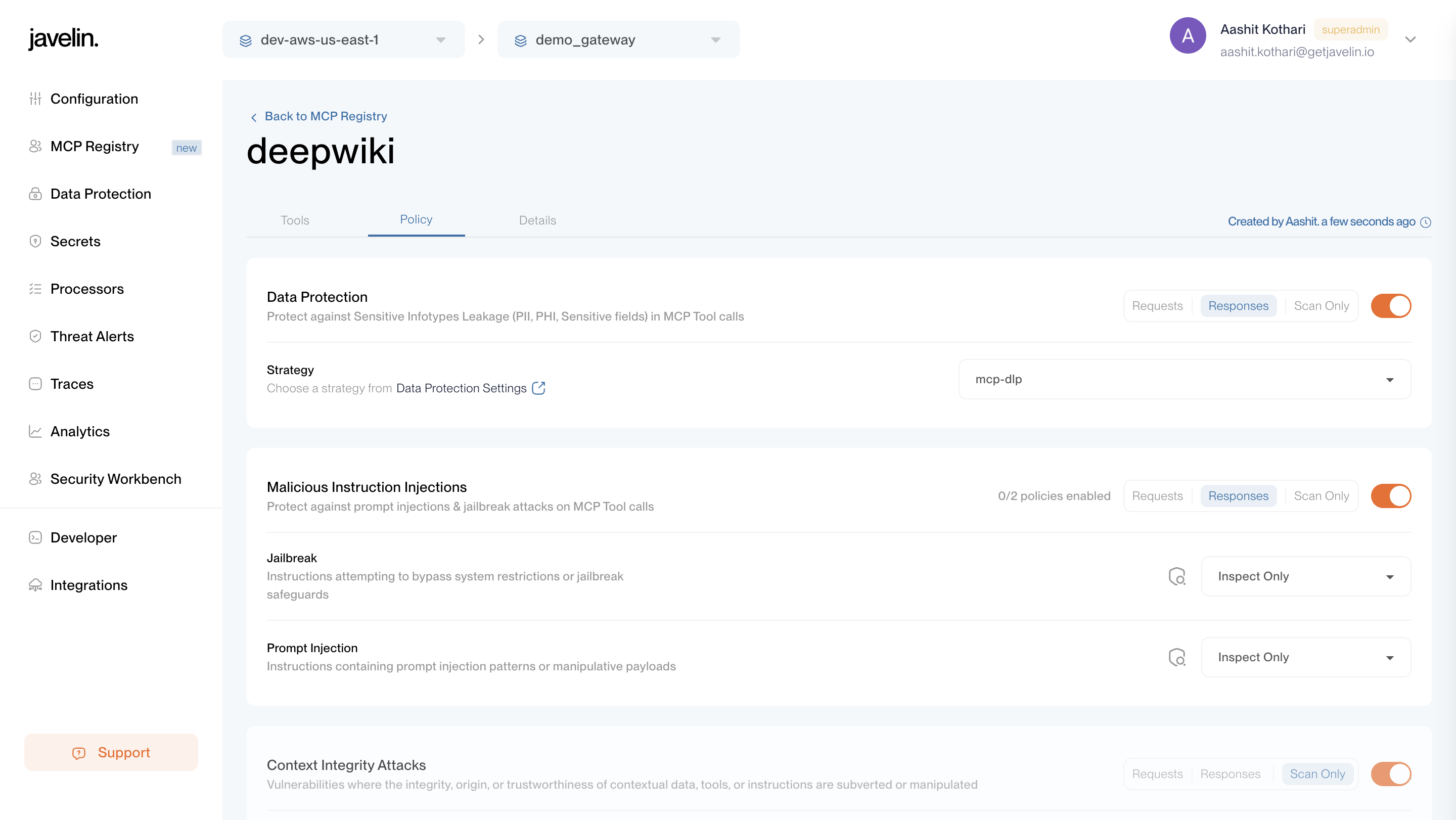
The Policy tab displays all MCP Registry-level policies currently applied.
Policies ensure safer usage of MCP tools by applying filters such as:
- Malicious Instruction Injections – Defends against prompt injection or jailbreak attempts.
- Data Protection – Prevents exposure of sensitive data like PII, credentials, or secrets.
- Security Filters – Defends against MCP tool vulnerabilities such as command injection, path traversal, secrets leakage, and SQL injection.
These registry-level guardrails are enforced after a tool response is received when requests are made using an application key.
For a detailed breakdown of policy fields and configurations, see the MCP Configuration Guide.
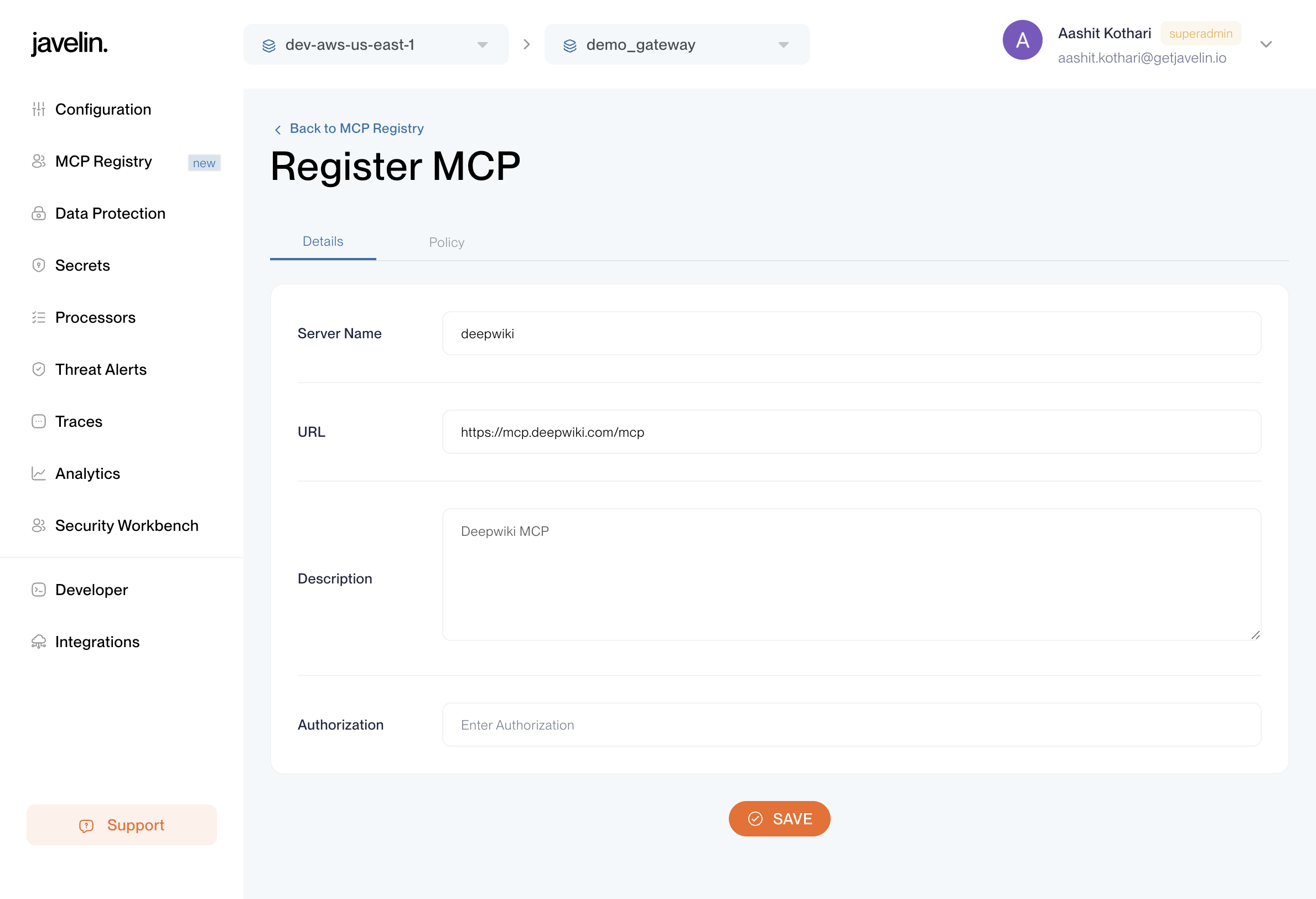
Details Tab
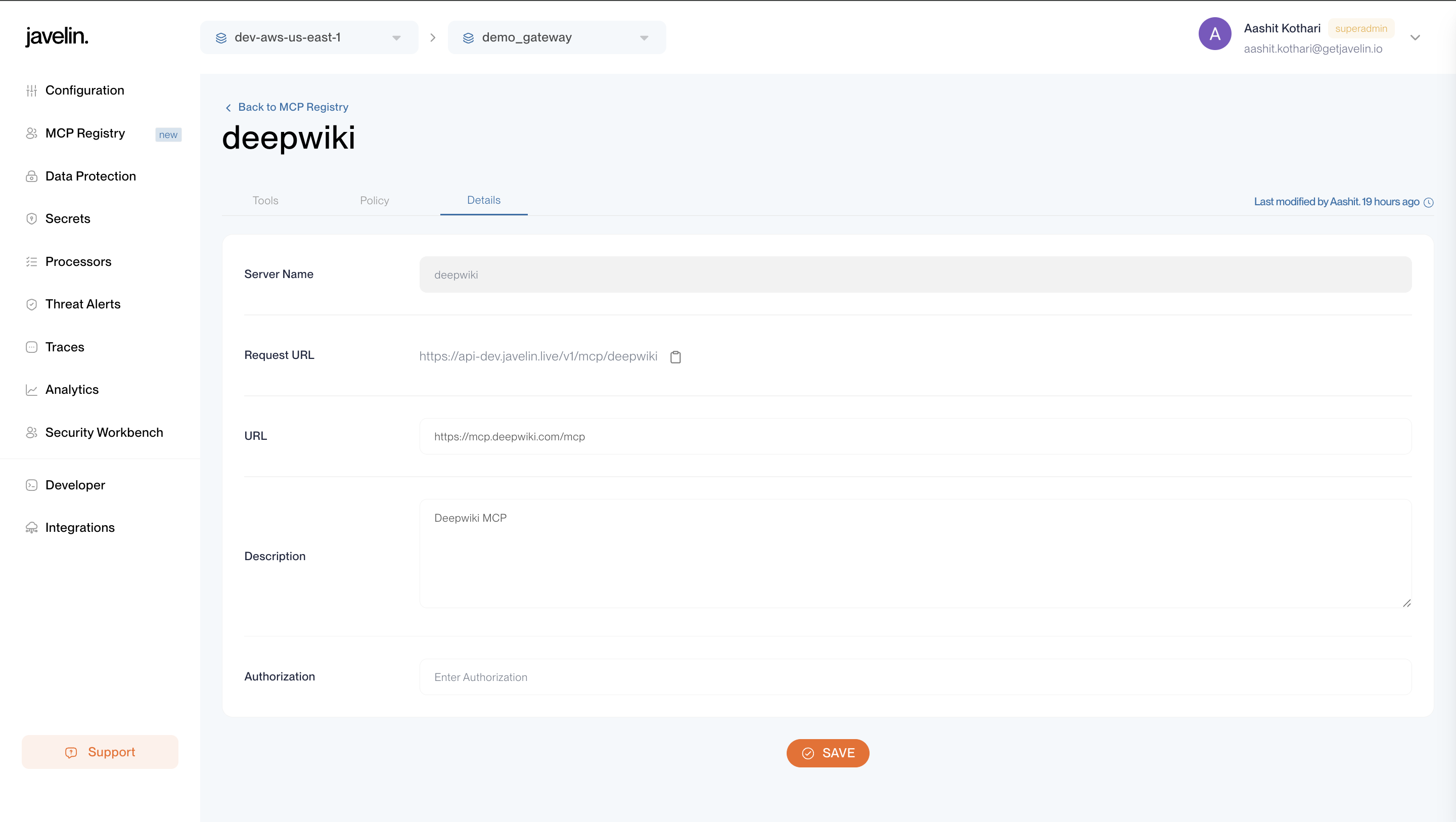
The Details tab provides the core configuration for your MCP Registry.
It includes:
- Name – Unique identifier for your MCP server (e.g.,
deepwiki,github). - URL – The base URL of the MCP server.
- Request URL – The endpoint Javelin uses to send MCP requests for this server.
- This URL is automatically generated after registration and is required when connecting LLMs to MCP tools.
- Example:
https://api.javelin.live/v1/mcp/deepwiki
- Description – A human-readable purpose or context for the MCP registry.
- Authorization Token – Token used to authenticate with the MCP server.
- Store this securely, as it may grant direct access to the MCP server’s tools.
- The token can be updated at any time if compromised.
This tab serves as the foundation for connecting Javelin to your MCP server, ensuring all requests are routed securely.
Application Graph Tab
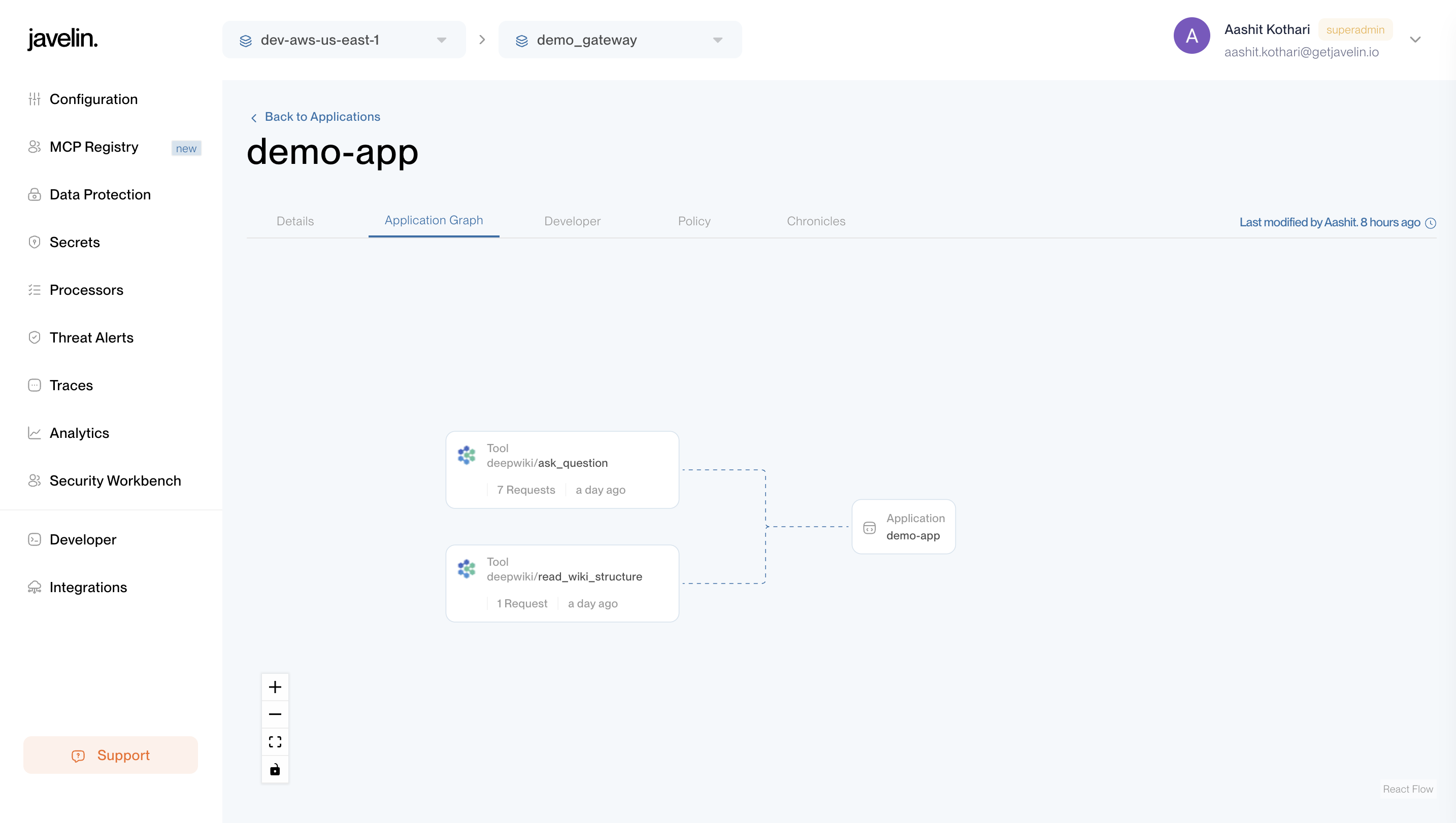
- Displays all MCP tools accessed via this application's key.
- Shows tool name, MCP server, number of requests, and last used in a graph format.
- Helps you analyze MCP tool usage patterns and identify high-traffic integrations.
Developer Key Requirement
To interact with MCP servers via Javelin, you need an Application Developer Key.
- This key is passed in the
X-Javelin-Apikeyheader when making requests. - To learn how to create an Application and generate Developer keys, see the Application Guide.
Hitting an MCP Server (Example: DeepWiki)
You can invoke MCP servers such as DeepWiki through an OpenAI LLM (e.g., GPT-4.1).
Below is an example curl request:
curl --location 'https://api-dev.javelin.live/v1/responses' \
--header 'Content-Type: application/json' \
--header 'Authorization: Bearer {{OPENAI_SECRET_KEY}}' \
--header 'X-Javelin-Apikey: {{APPLICATION_DEVELOPER_KEY}}' \
--data '{
"input": "List all tools which are supported in the 2025-03-26 version of the MCP spec.",
"model": "gpt-4.1",
"tools": [
{
"headers": {
"Authorization": "Bearer {{APPLICATION_DEVELOPER_KEY}}"
},
"require_approval": "never",
"server_label": "deepwiki",
"server_url": "https://api-dev.javelin.live/v1/mcp/deepwiki",
"type": "mcp"
}
]
}'
Explanation
- Authorization: Bearer OPENAI_SECRET_KEY → Authenticates with the OpenAI LLM provider.
- X-Javelin-Apikey: APPLICATION_DEVELOPER_KEY → Authenticates the request in Javelin and logs it under the Application.
- tools block → Connects the LLM to the MCP server (here:
deepwiki).- Authorization (inside tools block): Bearer APPLICATION_DEVELOPER_KEY → Authenticates requests made by the LLM to the MCP server via Javelin Gateway. This ensures the MCP tool invocation is also tracked under the same Application’s Chronicles.
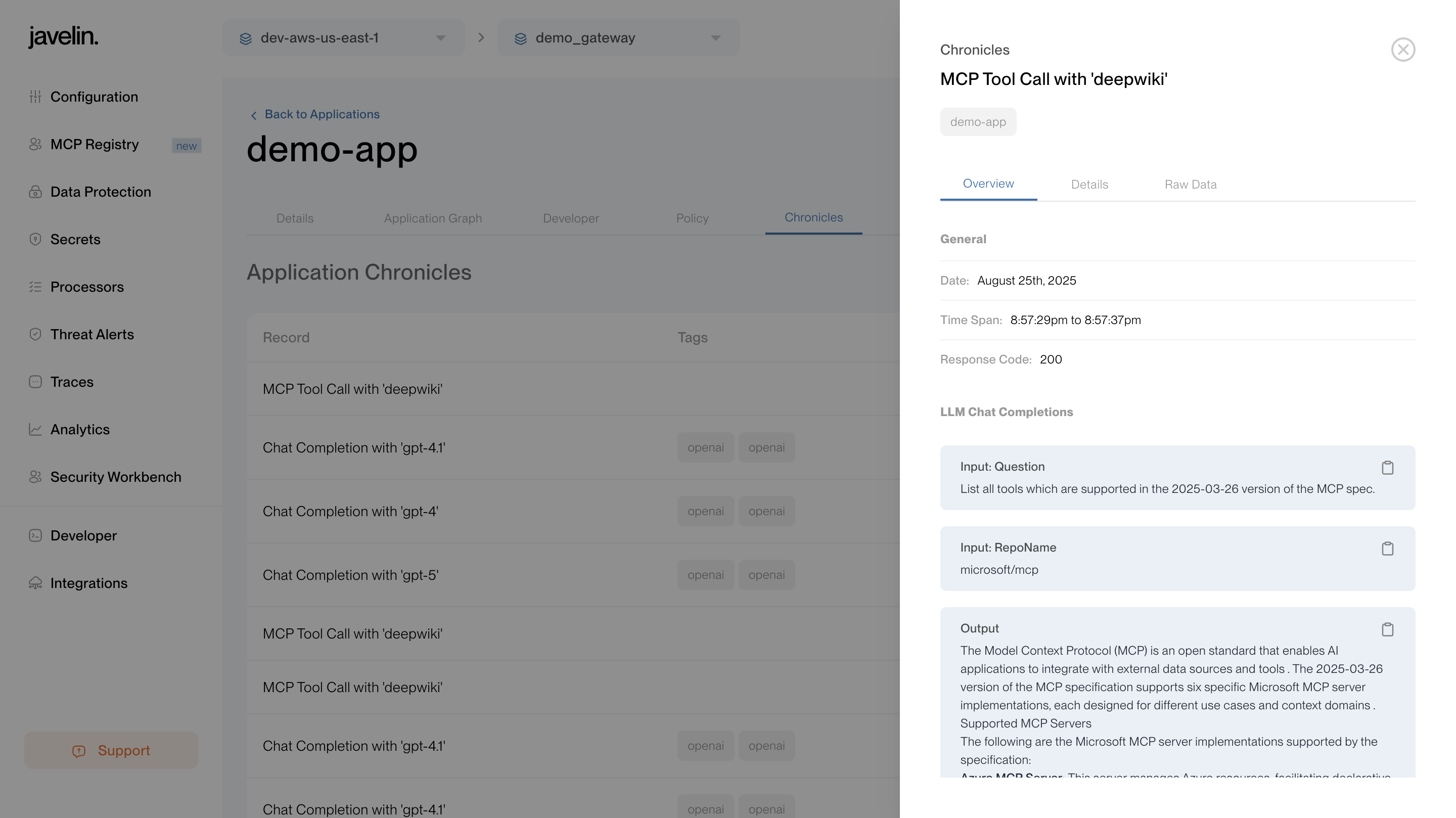
Chronicles for MCP Requests
Any request made to an MCP server using an Application Developer Key will appear in that Application’s Chronicles tab.
You will be able to see:
- Input sent in the request
- Output received in the response
- Tool invocations (e.g., DeepWiki calls)
- Guardrail checks
This ensures that all MCP-related activity is auditable under the Application whose key was used.