Alert Integration
Slack Alert Integration
To enable Slack alerting in Javelin, you'll need to configure a Slack webhook to allow Javelin to send messages to your Slack channel.
Refer to the Slack Webhook Setup Guide for step-by-step instructions.
1. Navigate to the Integrations Page
From the side navigation, select Integrations.
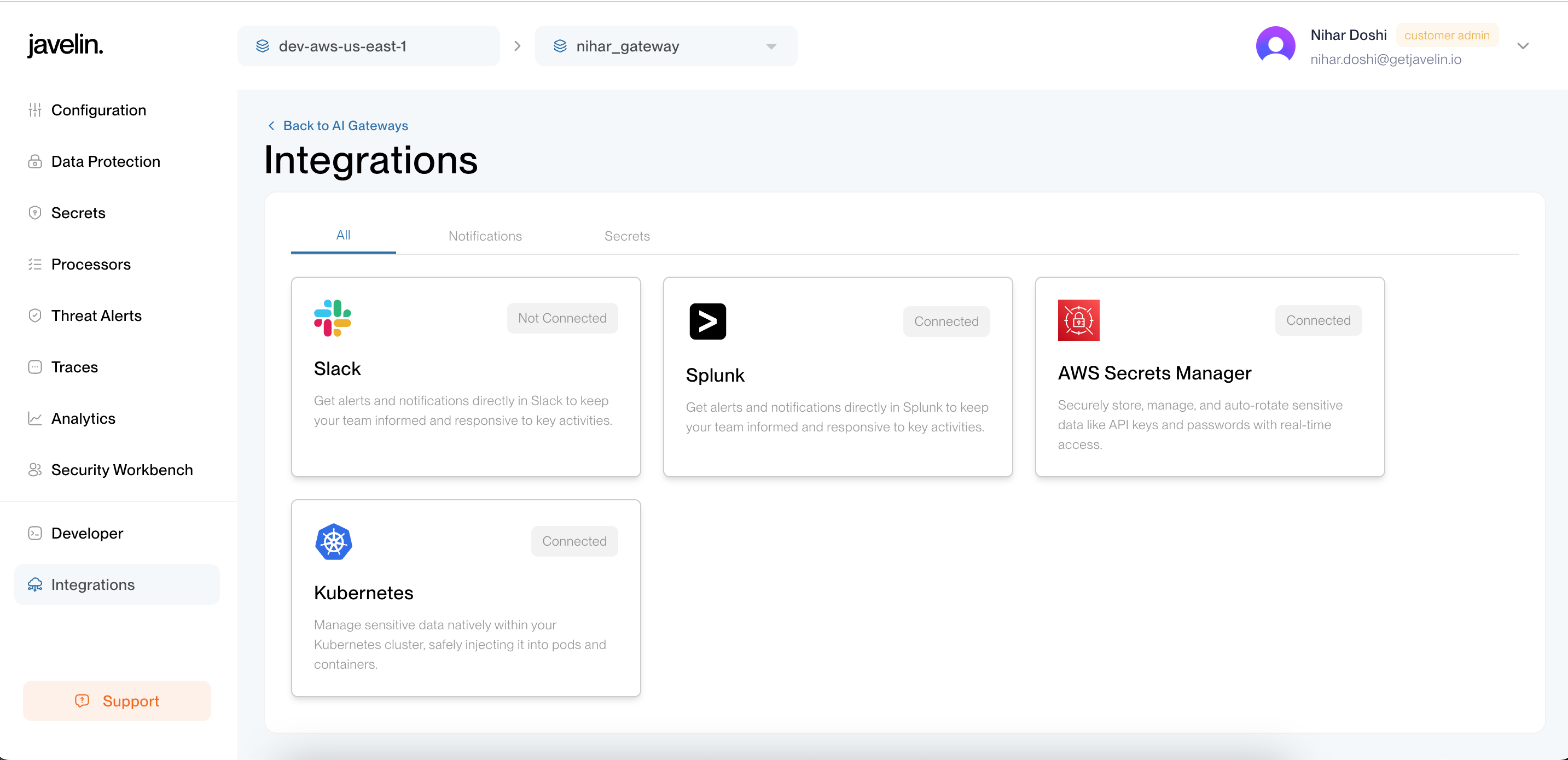
2. Configure the Slack Integration
Click on the Slack integration card and provide the required details, such as the webhook URL.
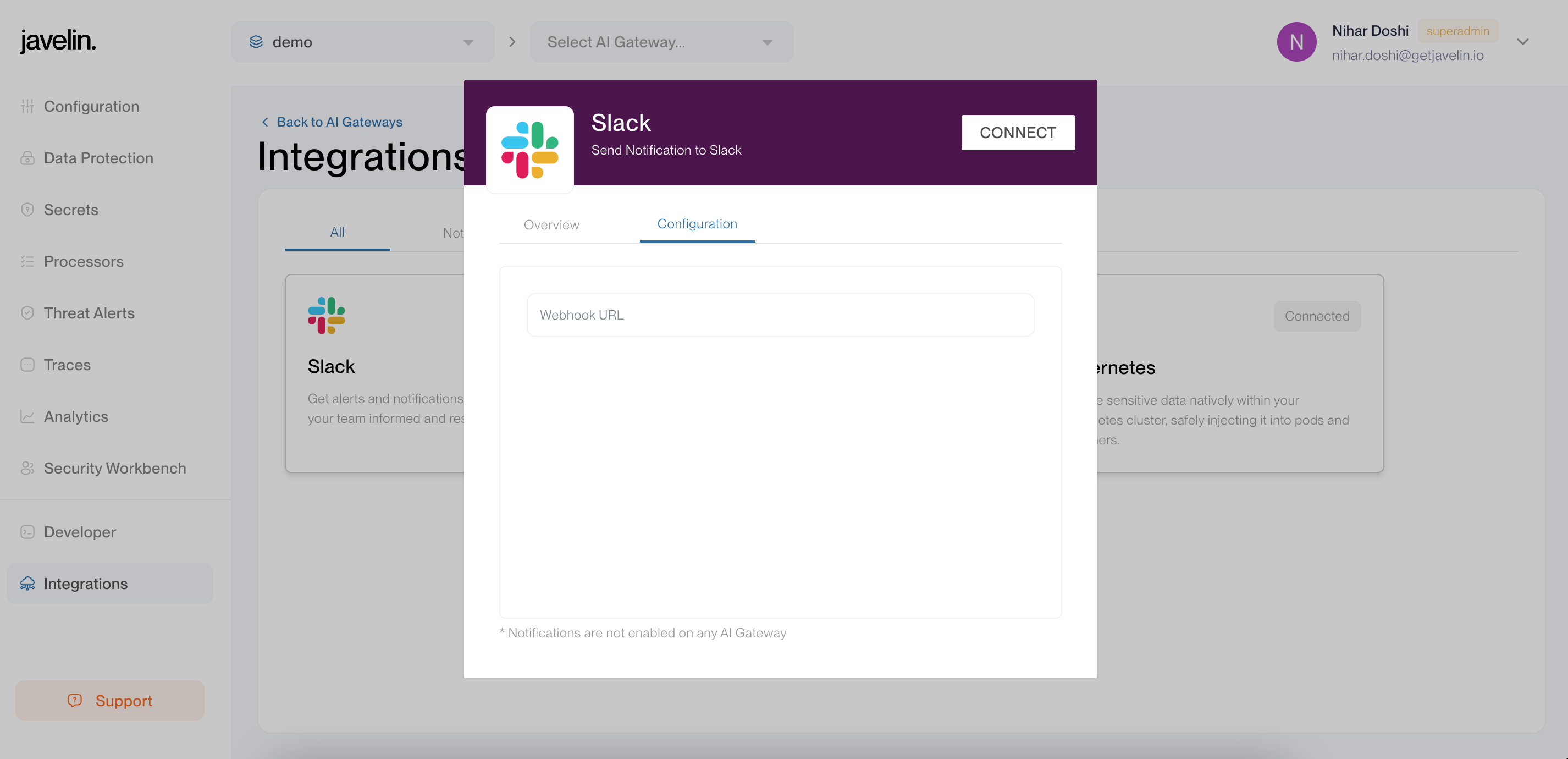
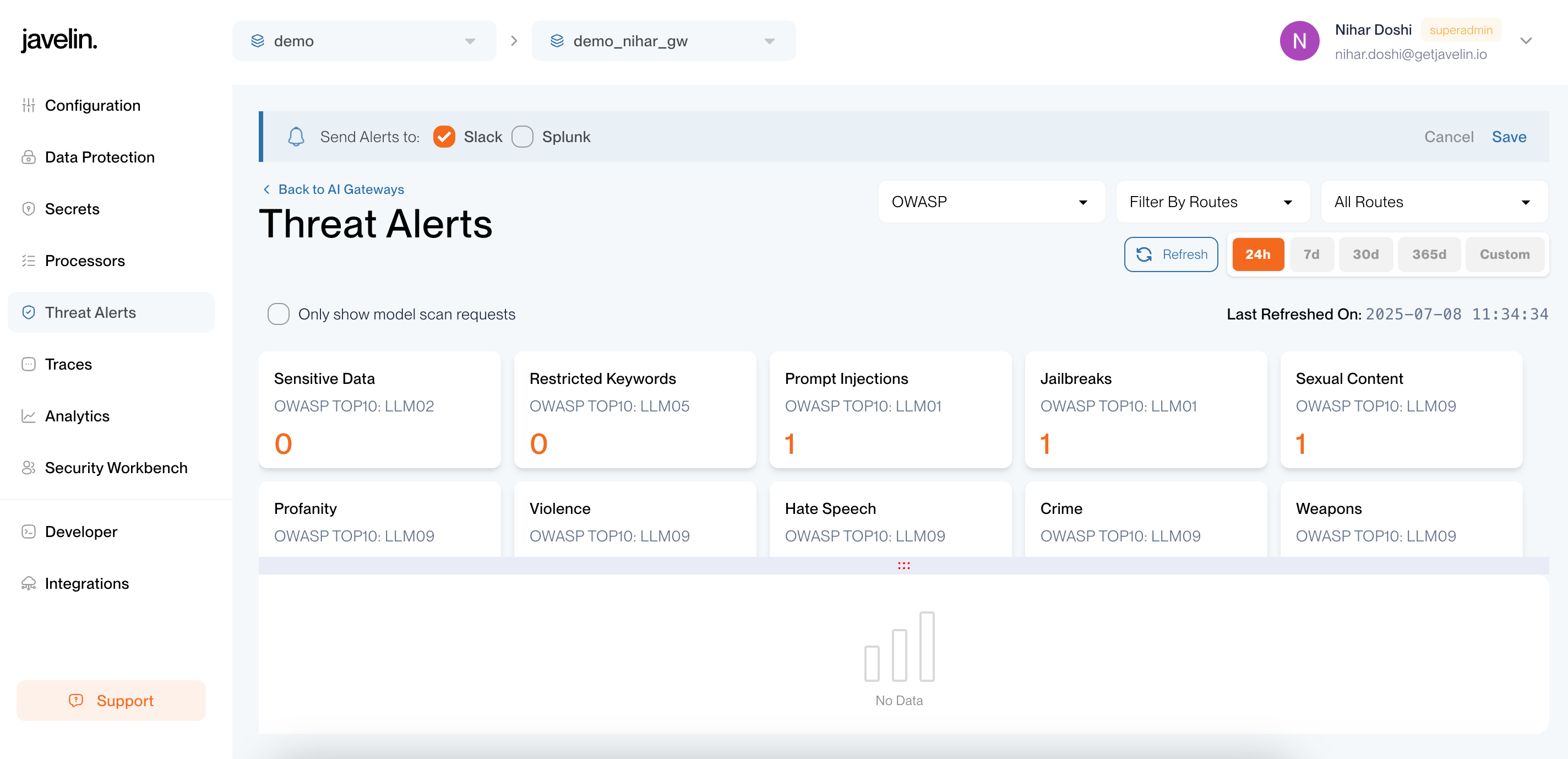
3. Enable Slack in Threat Alerts
To start receiving alerts in Slack:
- Go to the
Threat Alertspage. - Click
Manage Notificationfor your desired gateway. - Enable
Slackto send alerts for that gateway.
Splunk Alert Integration
To enable Splunk alerting in Javelin, you must configure the HTTP Event Collector (HEC) in Splunk. You'll need the following:
- Base URL of your HEC endpoint
- Authentication token
- A payload including required fields like
eventandsourcetype
Refer to the Splunk HEC Setup Guide for detailed instructions.
1. Visit the Integrations Page:
In the left-hand navigation panel, click on Integrations.

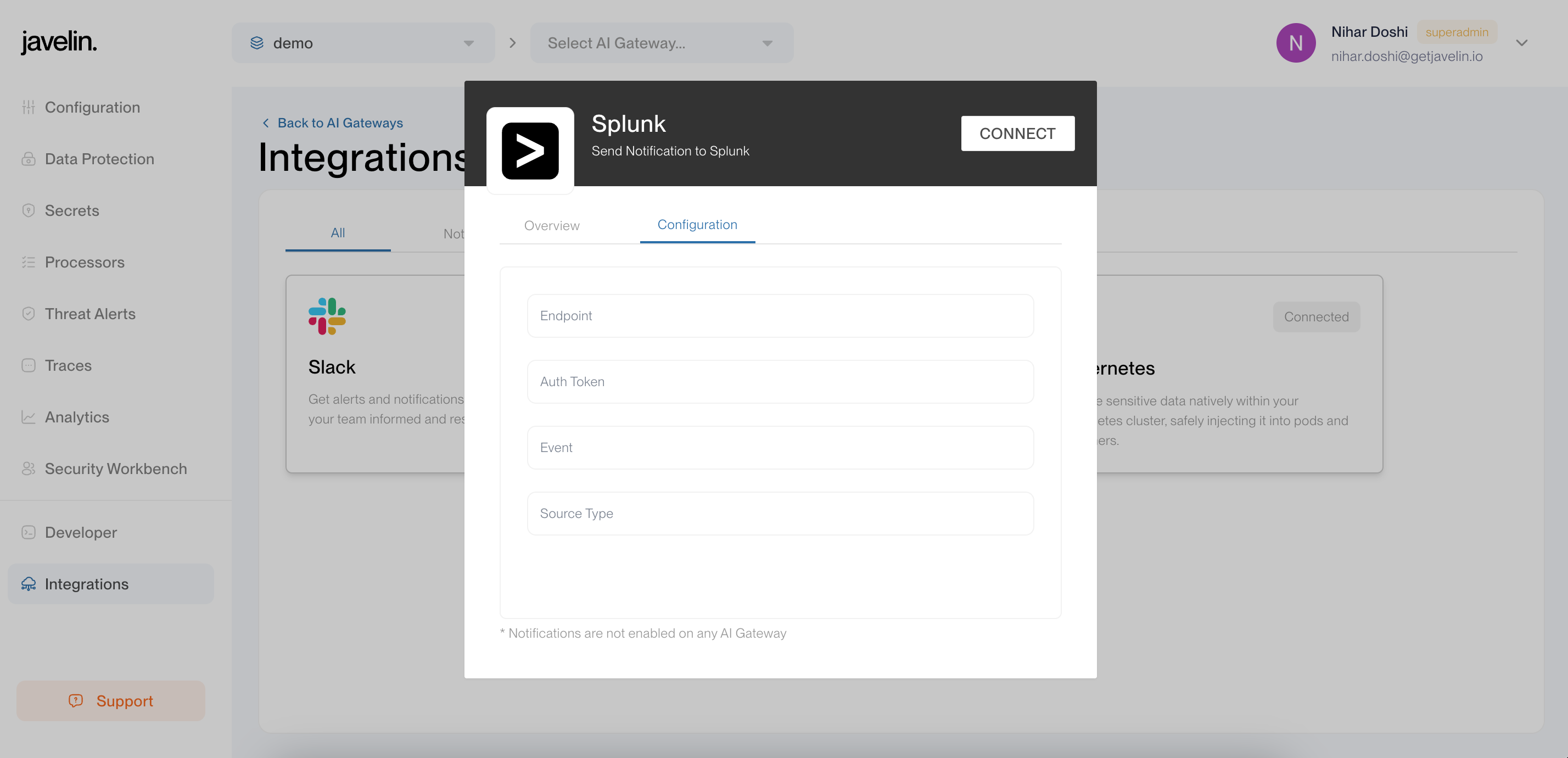
2. Select the Splunk integration
Click on the Splunk Integration card and fill in the following required fields: Endpoint, Token, Event, and Sourcetype.
- Endpoint:
https://<mysplunkserver.example.com>:<port>/services/collector/raw(By default, the port is 8088.) - Token: Your splunk token generated after configuring HEC.
- Event: You may set this to any descriptive value, for example: Javelin Trigger.
- Sourcetype: Your sourcetype configured during HEC setup (can be
manual).
Ensure that the sourcetype value matches the one configured in your Splunk HEC setup.
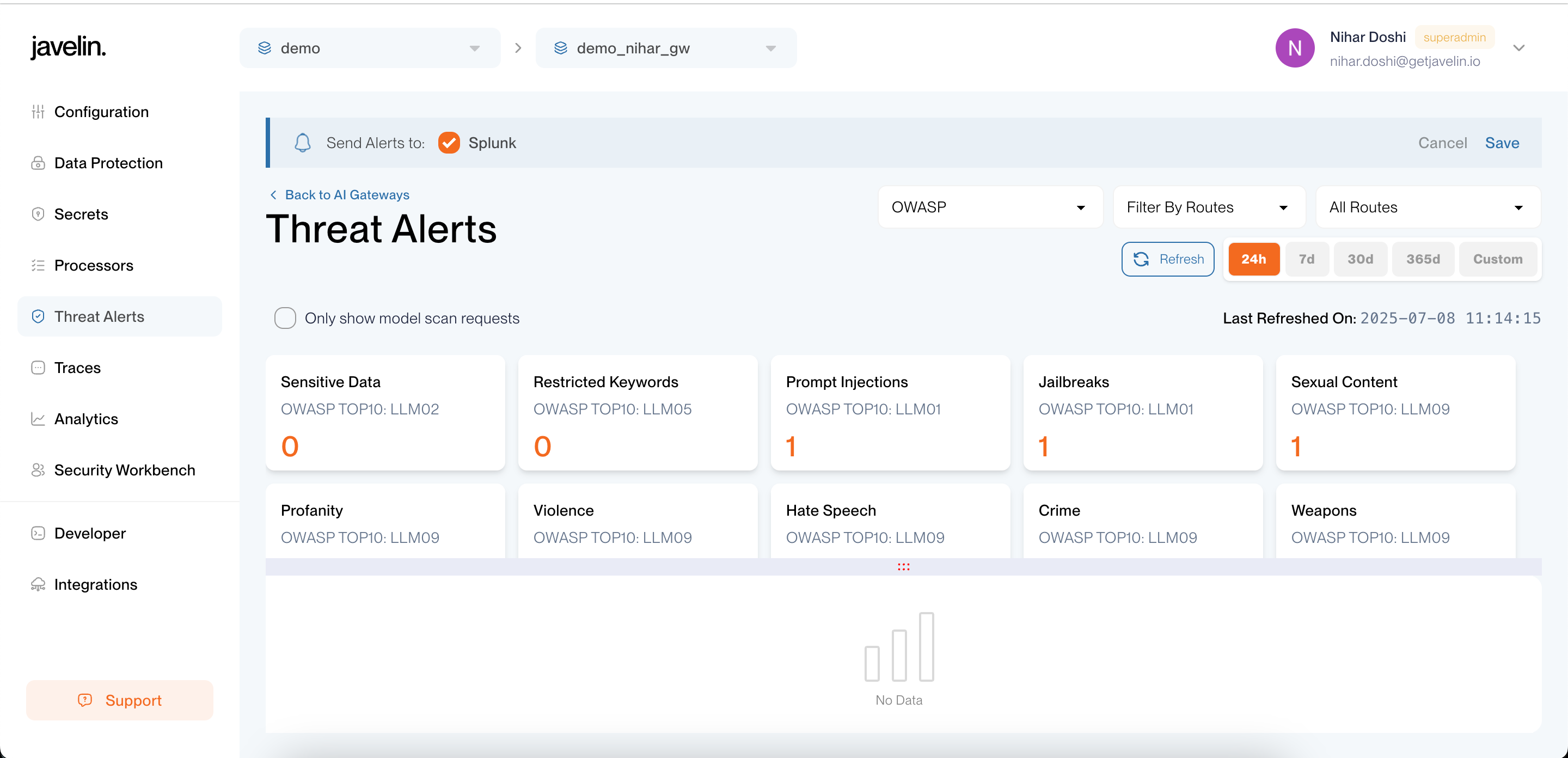
3. Move to Threat-Alert Page:
- Navigate to the
Threat Alertssection. - Click
Manage Notificationfor your chosen gateway - Enable
Splunkas the alert destination.
Advanced Configuration for Alert in Javelin
This feature is currently not supported on the web application. Please use the API directly to access this functionality.
By default, alerts in Javelin are generated per gateway. However, for more granular control over when alerts should be triggered, Javelin also supports advanced configurations via the trigger_condition field in the alert integration configuration.
🛠️ Supported trigger_condition Fields
The following fields are supported for fine-tuned alerting:
| Field | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
threats | array | Specify one or more threat types (e.g., ["prompt_injection_detected", "jailbreak_detected"]) to trigger alerts only for those threats. |
route_names | array | Specify one or more route names to restrict alerting to specific routes. |
gateway_ids | array | Specify one or more gateway IDs. This is the default behavior in the UI. |
application_ids | array | Specify one or more application IDs to limit alerts to specific applications. |
Click here to view the full list of supported threat types that can be used in the trigger_condition.threats array.
How to Configure
To apply trigger_condition filters, you must perform the following operation, passing the desired trigger_condition in request body.
1. Fetch Integration Details (GET Request)
Retrieve the integration configuration for which you want to add a trigger specification. Note the alert-id from the response.
curl --location '<your_domain_url>/v1/admin/integrations/config' \
--header 'x-javelin-apikey: <javelin-api-key>'
2. Update Integration with Trigger Condition (PUT Request)
Use the alert-id obtained from the GET call and the full existing JSON configuration. Add or modify the trigger_condition field as needed.
Ensure you copy the full existing config and only append the trigger_condition block as required.
curl --location --request PUT '<your_domain_url>/v1/admin/integrations/config/<alert-id>' \
--header 'x-javelin-apikey: <javelin-api-key>' \
--header 'Content-Type: application/json' \
--data '{
...your_existing_config,
"trigger_condition": {
"threats": ["prompt_injection_detected", "jailbreak_detected"],
"route_names": ["openai_gpt4_chat", "anthropic_claude"],
"gateway_ids": ["gwy1"],
"application_ids": ["app_xyz"]
}
}'
- All fields in
trigger_conditionare optional and can be used independently or in combination.
Example Event Payload (Splunk)
{
"Account ID": "<account-id>",
"Gateway ID": "<gateway-id>",
"Severity": "<severity>",
"Route Name": "<route-name>",
"Application ID": "<app-id>",
"Threat ID": "<threat-id>",
"Alert ID": "<alert-id>",
"Detected Threats": [
"Sensitive Data: Yes",
"Restricted Keywords: Yes",
"Regex Matches: [^.h.$]",
"Data Blocked: Yes",
"Sensitive Data Masked: Yes",
"Prompt Injection: Yes",
"Entropy Score: 0.93"
],
"event": "<event-name>",
"sourcetype": "<sourcetype>"
}